- Home
- Phd Apri sottomenù
-
Teaching
Apri sottomenù
- TRAINING RULES - 41st PHD Cycle
- Training activities 41st cycle
- Training activities 40th cycle
- TRAINING RULES - 40th PHD Cycle
- Suggested seminars and events
- Training activities 39th cycle
- Training activities 38th cycle
- Training activities 37th cycle
- Training activities 36th cycle
- Training activities 35th cycle
- Training activities 34th cycle
- Complementary courses a.y. 2022/23
- Complementary courses a.y. 2021/22
- Complementary courses a.y. 2020/21
- People Apri sottomenù
- Admission
- Partners
- Imola District
- Events
- Contacts
Training activities 40th cycle
Training activities for the PhD students of the 40th cycle
Teaching activities scheduled for 2024/25
All courses are available since the 1st year
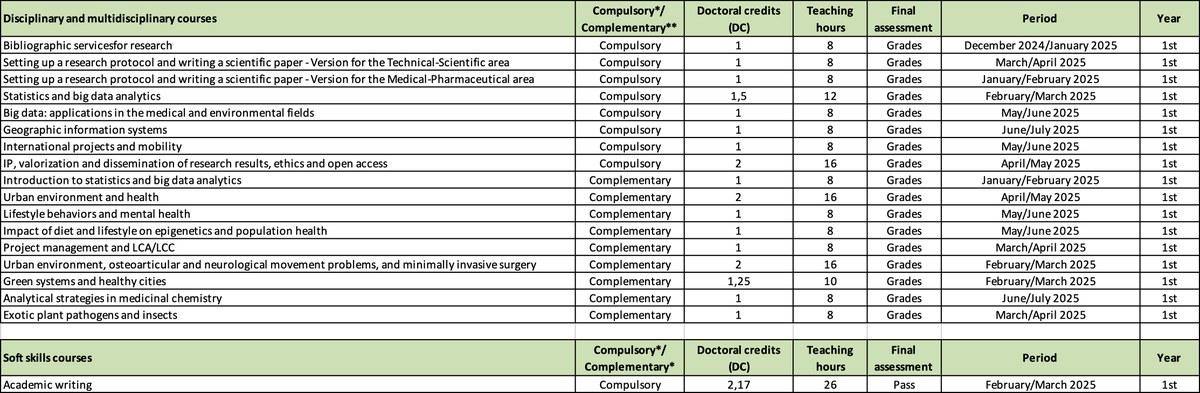
* Compulsory: compulsory training program common to all PhD students
** Complementary: complementary training program aimed at knowledge alignment and in-depth analysis of various topics (courses to be identified with the support of the supervisors and the academic board)
Courses Timetable
12 MARCH 2026
Complementary
PublishedExotic plant pathogens and insects mod. 1 (Prodi)
18 MARCH 2026
Complementary
PublishedExotic plant pathogens and insects mod. 2 (Dindo)
25 MARCH 2026
Complementary
PublishedProject management and LCA/LCC mod. 2 (Santolini)
01 APRIL 2026
Compulsory
PublishedIP, valorization and dissemination of research results, ethics and open access mod. 1 (Benni)
08 APRIL 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment and health” mod. 1 (Gori)
09 APRIL 2026
Compulsory
PublishedSetting up a research protocol and writing a scientific paper - Version for the Technical-Scientific area (Barbaresi)
14 APRIL 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment and health” mod. 1 (Gori)
16 APRIL 2026
Compulsory
PublishedSetting up a research protocol and writing a scientific paper - Version for the Technical-Scientific area (Barbaresi)
21 APRIL 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment and health” mod. 1 (Gori)
23 APRIL 2026
Compulsory
PublishedIP, valorization and dissemination of research results, ethics and open access mod. 4 (Benni)
06 MAY 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment and health” mod. 2 (Toselli)
08 MAY 2026
Complementary
PublishedProject management and LCA/LCC mod. 1 (Bragadin)
13 MAY 2026
Complementary
PublishedLifestyle behaviors and mental health (Menchetti)
15 MAY 2026
Compulsory
PublishedIP, valorization and dissemination of research results, ethics and open access mod. 3 (Bragadin)
27 MAY 2026
Complementary
PublishedLifestyle behaviors and mental health (Menchetti)
29 MAY 2026
Compulsory
PublishedIP, valorization and dissemination of research results, ethics and open access mod. 1 (Bovo)
04 JUNE 2026
Compulsory
PublishedInternational projects and mobility mod. 1 (Dindo)
09 JUNE 2026
Compulsory
PublishedBig data: applications in the medical and environmental fields (Gori)
10 JUNE 2026
Compulsory
PublishedInternational projects and mobility mod. 2 (Bordoni)
11 JUNE 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment, osteoarticular and neurological movement problems, and minimally invasive surgery" mod. 3 (Pillastrini)
12 JUNE 2026
Compulsory
PublishedBig data: applications in the medical and environmental fields (Gori)
15 JUNE 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment, osteoarticular and neurological movement problems, and minimally invasive surgery" mod. 1 (Berti)
18 JUNE 2026
Complementary
PublishedImpact of diet and lifestyle on epigenetics and population health (Astolfi)
22 JUNE 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment, osteoarticular and neurological movement problems, and minimally invasive surgery" mod. 2 (Platano)
23 JUNE 2026
Compulsory
PublishedGeographic information systems (Torreggiani)
25 JUNE 2026
Complementary
PublishedImpact of diet and lifestyle on epigenetics and population health (Astolfi)
30 JUNE 2026
Compulsory
PublishedGeographic information systems (Torreggiani)
02 JULY 2026
Complementary
PublishedUrban environment, osteoarticular and neurological movement problems, and minimally invasive surgery" mod. 4 (Zaffagnini)
LOG IN TO THE PLATFORM TO DOWNLOAD THE TEACHING MATERIAL OF THE COURSES
Course contents
Bibliographic servicesfor research (8 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours): Enrica Santolini
Mod. 2 (4 hours): Davide Gori
Main on-line tools for bibliographic resources that can be accessed through the library system of the university of Bologna: book and journals catalogues, databases. Practical exercises on the tools presented. Students will achieve the methodology for building evidence-based strings for making research in medical literature. Students will discuss together the basic principles for appraising a scientific article. Contents: Sources of information and information retrieval; How to find books and journals: SBN-Ubo and ACNP Opacs; How to find articles: databases (CAB Abstracts, WOS and Scopus, Proquest, AlmaStart); Reference manager (Zotero); Citation and citation styles. How to build evidence based search strings and filters for the identification of all relevant studies to answer clinical questions. Basic principles for appraising and evaluating the quality of a scientific article. A practical example and discussion with the class of literature search in PubMed and/or other databases.
Setting up a research protocol and writing a scientific paper (8 hours)
Version for the Technical-Scientific area: Alberto Barbaresi
Version for the Medical-Pharmaceutical area: Andrea Turolla
At the end of the course, the student has knowledge, as far as he is competent, relating to the field of research methodology and will be able to conduct a critical appraisal of a clinical trial/observational study. Moreover, the course aims at presenting the purpose, goals and requirements of scientific papers, their structure and how each section should be prepared. Course contents: Characteristics of the different study designs; Selection of subjects for study; Sources of error and of bias; Confounding; Critical appraisal of some research protocol; research question or hypothesis; feasibility of the project (costing; resources, expertise in methodology, statistics, etc.). Structure of a scientific paper; structure in five sections: Introduction, Materials and methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusions; Abstract and appendices. Introduction: context, need, task, and object. Materials and methods: Study design, Setting, Sample or participants (inclusion and exclusion criteria), Interventions and control group, Measures, Outcomes, Statistical analysis. Results and discussion; Description of sample/participants, Main outcome measures, Other findings organized in paragraphs by relevance; Discussion: Summary with main findings, Interpretation of results, Comparison with available literature, Directions for further research, Limitations of the study; Conclusion: most important outcomes, perspectives.
Statistics and big data analytics (12 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours): Alberto Barbaresi
Mod. 2 (8 hours): David Neil Manners
The PhD student will acquire the bases of big data analysis, familiarizing with the most common techniques for storing, managing and using of unstructured data with a specific attention to the extraction and analysis of information in biological and environmental fields. By the end of the course, the student will be able to organise and prepare data for scientific research, and to visualise and analyse it using R. The course will emphasise applications to real data sets. Contents: the course presents different case studies to show techniques for feature selection and for the big data management and analyses chosen for this course. Student will be encouraged to present and discuss, with the teacher and other students, his/her own research issues concerning on data/big data management and analysis. 1) Project and data management - Outline of main considerations regarding data management for scientific projects, and brief review of useful software packages; 2) Data type and structures - Overview of data types and data structures, with special emphasis on the R language; 3) Outline of R - Introduction to the R language, including fundamental elements of grammar including syntax and control structures, and use of the Rstudio GUI; 4) Data wrangling - Description of processes needed to prepare data for visualisation and analysis, including importing and exporting data sets, data cleaning, and reformatting for easy processing; 5) Data visualization - Graphical techniques for visualising distributions of and correlations between categorical and continuous variables; 6) Data modelling, analysis and statistics - A brief review of techniques to summarise and simplify data using descriptive and inferential statistics. Teaching methods: Conventional lessons and computer laboratories, conducted in a computer room using terminals with required software pre-installed.
Big data: applications in the medical and environmental fields (8 hours)
Davide Gori
The course focuses on the role of big data in modern epidemiology and in the environmental field and as a way to tackle modern epidemics (i.e. chronic diseases and aging). Contents: Construction of database to manage population based data. Practical examples of data construction and management using statistical packages. Students will learn the basis of the utilization of big data in medicine and in the environmental field. Students will undergo practical laboratories for data construction and management using statistical packages.
Geographic information systems (8 hours)
Daniele Torreggiani
The PhD student will acquire the theoretical and practical bases of maps and geographic information systems (GIS), and will be able to use both raster and vector layers, perform data spatialization and data analysis and geoprocessing in in GIS environment. Contents: Fundamentals of cartography, introduction to digital maps and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS software: main commands and functions, geodata: sources and online services. GIS practicals with GIS software: loading, management and queries on vector and raster maps, reclassification. Reference system definition and transformation. Creating and editing of maps and attribute tables, feature selection based on attributes and location, join and spatial join. Main geoprocessing functions: proximity analysis, buffer analysis, overlay mapping, clipping, merging. Importing GPS data into a GIS. Print and exporting: legend, dataframe management.
International projects and mobility (8 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours) Maria Luisa Dindo
Mod. 2 (4 hours) Alessandra Bordoni
EU competitive projects represent an important opportunity for researchers. Competition is increasing and it is important to learn and adopt strategies that could improve the success rate. The content of the course is about the explanation of these strategies, starting from the preparation of the proposal and concluding with the successful submission of the final report to the EU Commission. Moreover, the course aims to illustrate to the students of the SSSV course the opportunities for international mobility offered to them, taking into account that a stage abroad (in an appropriate place and with a study / research program well in line with the thesis topic) represents an essential moment in the training of a PhD student. The course also aims to briefly illustrate the results of some concrete experiences, with the aim of better directing the PhD students towards the choices they will be able to make. Contents: - International projects: aspects related to the preparation of the proposal, considering the standard template; aspects related to the management of the Consortium, including the preparation of the Consortium Agreement, the IPR and exploitation of results; relationship between the Coordinator and the EU Commission, from the grant agreement to the final report. - International mobility: 1. Requirements for stays transferred and to obtain the related increase in scholarship; 2. Main mobility programs (e.g. Erasmus plus, Marco Polo, Brown University); 3. Other opportunities abroad; 4. Reference sites and contacts; 5. Previous experiences abroad of PhD students (with the teacher as tutor), with suggestions to better exploit this opportunity.
IP, valorization and dissemination of research results, ethics and open access (16 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours): Marco Bovo
Mod. 2 (4 hours): Stefano Benni
Mod. 3 (4 hours) Marco Alvise Bragadin
Mod 4 (4 hours): Stefano Benni
At the end of the course the PhD student learns: - the concept of intellectual property related to research results, what the intellectual property (IP) is and the main procedures to protect it and exploit it; - the fundamentals of entrepreneurship and the main phases of development of a business idea and relevant tools; - the main elements of research ethics governing the standards of conduct for scientific researchers, standards which promote not only the aims of research, such as knowledge, truth, and avoidance of error, but also the values essential to collaborative work such as trust, accountability, mutual respect and fairness (i.e. concerning authorship, copyright, patenting); - the principles, goals, benefits and e practices of open access and open science; - the key aspects of the structure of an effective presentation and dissemination of research findings and achieves the main communication skills to present a research to the scientific community. Contents: - Legal rights related to the IP, IP valorization, University policies and services to support IP protection and valorization. - Introduction to entrepreneurship, identifying and evaluating new business ideas, Business Plan and business model; Entrepreneurial mindset; Creative research of ideas, evaluation of entrepreneurial opportunities, entrepreneurship paths and financing. - the European Code of conduct for research integrity, a list of ethical issues concerning privacy and data protection, the human subjects protection, animal care and use, conflict of interest, environmental impact and other possible scientific misconduct of the proposed research. - Open access publications, open data and FAIR principles; - Fundamentals of communication for academic presentations and dissemination; Analysis of presentations of research findings; Process of outlining the structure of a scientific presentation; Workshop for the application of the theoretical contents.
Academic writing (26 hours)
CLA (Academic Language Center)
The course aims to provide specific skills in written and spoken communication of English and aimed at writing articles and oral presentations for conferences and congresses. The course includes the production of written and oral papers and the completion of selected modules of the Epigeum interactive course.
Introduction to statistics and big data analytics (8 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours): Marco Bovo
Mod. 2 (4 hours): David Neil Manners
The student will acquire the bases of statistics, either from a methodological and an applied perspective, for the analysis of data of different nature. In particular, the student will be able to use distributions and graphs, select and compute the most appropriate summary statistics, identify, and measure the strength of the relation between two characters, set linear regression and correlation analysis. Moreover, the PhD student will acquire the bases of big data analytics, also with references to basic elements of data management and data analysis software languages.
Urban environment and health (16 hours)
Mod. 1 (12 hours) Davide Gori
Mod. 2 (4 hours) Stefania Toselli
At the end of the course the PhD student is able to show evidence about how social and physical environment and individual behaviours affect health. Moreover, PhD Students will learn and analyze the role of overweight and obesity as current public health emergencies, ad their role in the genesis of the most important metabolic syndromes. Students will also discuss the role of the different determinants of health inequalities, along with the strategies to contrast overweight and obesity. The course also aims at providing knowledge for the assessment of health status and any risk factors related to weight, body composition, and body fat distribution in children, adults and the elderly, and knowledge about the contribution of genetic and environmental factors to nutritional disorder: consideration of determinants within a multilevel framework and strategies for health promotion. Contents: - Introduction to Epidemiology and Public Health; Conceptual Models of Social Determinants of health; Social and economic environment as determinant of health; Physical environment as determinant of health; Social support networks as determinants of health; Person's individual characteristics and behaviours as determinants of health. - overweight and obesity as public health epidemics, data coming from Italian, European and worldwide scientific literature; differences in prevalence of obesity and inequalities, ways to tackle and contrast obesity. - Evaluation of nutritional status and of health risk indicators (weight status, body fat distribution, body composition, somatotype); Body composition variations during growth and in ageing: genetic and environmental influence.
Lifestyle behaviors and mental health (8 hours)
Marco Menchetti
The course focuses on the study of lifestyles as a major determinant of mental health. The course deals with the various ways in which mental health is conditioned by lifestyles, with reference to physical activity and relationships with healthy urban environments. Contents: role of lifestyle and of interventions related to physical exercise in helping to improve mental health and the outcomes of depression; physical exercise as a safe and effective augmentation to antidepressant therapy.
Impact of diet and lifestyle on epigenetics and population health (8 hours)
Annalisa Astolfi
The course in Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Epigenetics and Population Health will provide the basic knowledge on the influence of diet, nutrition and lifestyle on health maintenance, focusing on the effects on gene expression and epigenetic modifications. The course will cover the fundamentals of genetics and epigenetics (methylation and histone modifications), the interaction of foods and nutrients with gene expression and epigenetic modifications, the relationship between diet and lifestyle with gene expression and global health and between the microbiome and epigenetic profile.
Project management and LCA/LCC (8 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours) Marco Alvise Bragadin
Mod. 2 (4 hours) Enrica Santolini
Project management aims at delivering efficiently industrial projects. Project Management body of knowledge is a set of well-known skills and techniques of capital importance for owners, designers, managers and other players of the building construction process. Main concepts of European and Italian Occupational Health and Safety (OH & S) laws are presented, especially focusing on the construction sector. Moreover, the course addresses the evaluation of the sustainability of building projects and other products and processes using the Life Cycle Cost Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment. Contents: - The most important knowledge areas of project management needed in the construction sector and in manufacturing industry. - The historical development of the implementation of these concepts in Europe and Italy, addressing the directives 89/391/EEC, 92/57EEC and their Italian implementation of the consolidate law, the Italian republic decree no. 81/08. - Main concepts of Life Cycle Cost and Life Cycle Assessment, focusing on the construction sector and other products and processes.
Urban environment, osteoarticular and neurological movement problems, and minimally invasive surgery (16 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours) Lisa Berti
Mod 2 (4 hours): Daniela Platano
Mod. 3 (4 hours): Paolo Pillastrini
Mod. 4 (4 hours): Stefano Zaffagnini
At the end the PhD student has acquired the clinical tools for the evaluation of musculoskeletal function and the evaluation of outcomes for the main problems of the locomotor system, also in correlation to social participation (environment and architectural barriers), and the principles of instrumental functional assessment techniques in laboratory and external environment. The course also focuses on the mobility of subjects affected by different kinds of injuries and on their functional clinical evaluation, in relation to the urban environment and architectural barriers. Moreover, the course addresses innovative diagnostic tools and targeted treatments, and minimally-invasive procedures nowadays available to clinician and surgeons, allowing better recovery and patients satisfaction, with particular reference to the orthopedic field, where technology has given the possibility to identify the best treatment for every patient, with "tailored" surgeries. Contents: - Kinesiological evaluation of the musculoskeletal system (ROM evaluation: active and passive and manual muscle test). Evaluation scales (activities and participation in the social environment). Instrumental functional evaluation. Movement analysis. Baropodometry. Kinematic analysis with wearable inertial sensors. - International Classification of Functioning: General Principles; The Mobility of subjects with Brain Injuries; The Mobility of subjects with Spinal Cord Injuries; The Mobility of subjects with Lesions of the Extra-Piramidal System. - Technologies and devices that have improved the accuracy of the surgeons in the operating room reducing the possibility of surgical complications and pain, and helping people with a handicap such as amputation to obtain a faster recovery and prosthesis customized and osteo-integrated.
Green systems and healthy cities (10 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours) Alberto Barbaresi
Mod. 2 (6 hours) Davide Gori
At the end of the course the PhD student acquires the basic knowledge concerning the planning of urban green areas and the technological aspects related to green roofs, rooftop gardens and green walls. Moreover, PhD Students learn the role of urban programming and green spaces as a mean of improving health, and discuss the role of “neighborhood” and the role of smart cities as a mean for tackling health inequalities. Contents: - Fundamentals of land-use planning in urban areas; The role of green systems for environmental quality in urban areas; Green roofs and walls for the integration of green systems in buildings: classifications of green roofing and green walls; elements and layers constituting the sub-system; materials and components; load analysis; Analysis of study cases. - Neighborhood and its importance in the development of health inequalities. The importance of urban programming and the role of smart cities. Green spaces and healthy cities.
Analytical strategies in medicinal chemistry (8 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours) Laura Mercolini
Mod. 2 (4 hours) Michele Protti
At the end of the course, the PhD student possesses: - the basis theoretical knowledge on the main techniques and methods used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of bioactive compounds in samples of different origins. - The basic notions on sustainable approaches applied to analytical strategies, fulfilling the goal of sustainable development, to achieve more eco-friendly analytical platforms in the medicinal chemistry field, through technological and methodological approaches. Contents: - principles, purposes and problems peculiar to the pharmaco-toxicological analysis applied to the therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), determination of bioactive compounds in herbal matrices and environmental samples. main advanced instrumental analytical techniques, and related analytical methods, to identify and quantify drugs and metabolites in the most significant biological matrices for TDM purposes (for example whole blood, plasma and serum). analysis of bioactive compounds in samples of natural origin (e.g. herbal samples) and in environmental matrices. recent applications, relevant in the scientific literature. - overview of the principles of green chemistry applied to analytical methodologies (with a focus on bioanalysis). existing opportunities for greener sample pretreatment and environmentally-sound chromatographic methods for advanced analysis in the field of medicinal chemistry. The most up-to-date analytical approaches will be discussed taking into account the main requirements for a sustainable development. Strategies for the reduction of labour and energy consumption of analytical procedures. Overview on the development of smart, alternative sampling and sample treatment techniques, as well as the miniaturisation of the analytical equipment and pre-analytical protocols.
Exotic plant pathogens and insects (8 hours)
Mod. 1 (4 hours) Antonio Prodi
Mod. 2 (4 hours) Maria Luisa Dindo
The course provides basic information about the most important exotic plant pathogens emphasizing those that are insect transmitted, since they represent a relevant threat to agricultural, landscape and urban environments, and about the importance and need for a correct management with the least possible disruption to the diverse ecosystems and the least hazard to people, animals, and environment. The PhD students will also learn how insects spread from one area to another, the mechanisms of the invasiveness of some species and the resulting damage, with its repercussions, the sustainable methods of prevention and control of exotic insects and the structure and activity of intergovernmental organizations, the aims of which include preventing and stopping the phenomenon. Contents: - Exotic plant pathogens potentially relevant for the Italian environments. Basic elements to formulate a correct pathogen identification (diagnostic) based on symptoms and on analytical procedures. Basis for the understanding, interpretation, selection, development and application of the most effective methods of management of selected exotic plant pathogens to have the smallest environmental impact according with the diverse agroecosystems. Practical tools to reduce the impact of these pathogens on both human health and environment. - mechanisms of the diffusion of insects into new areas and enabling certain alien species to naturalize and become invasive in the countries of introduction. Case studies will be presented and dangers that invasive insects entail for agriculture, the environment and, in some cases, for health of humans and domestic animals will be highlighted. Sustainable invasive species management methods (including biological control) will be illustrated.